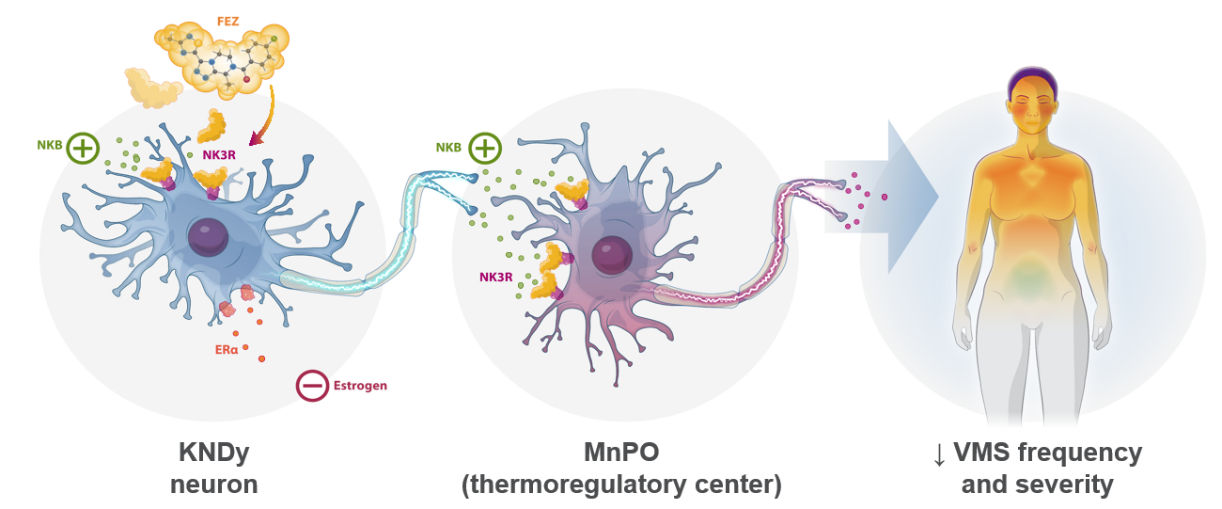
Fezolinetant is a selective neurokinin 3 receptor (NK3R) antagonist that blocks binding of neurokinin B (NKB) to kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons to modulate neuronal activity in the thermoregulatory center, helping to restore thermoregulatory balance
Restoration of thermoregulatory balance by fezolinetant:15
Figure 1. Normal thermoregulation
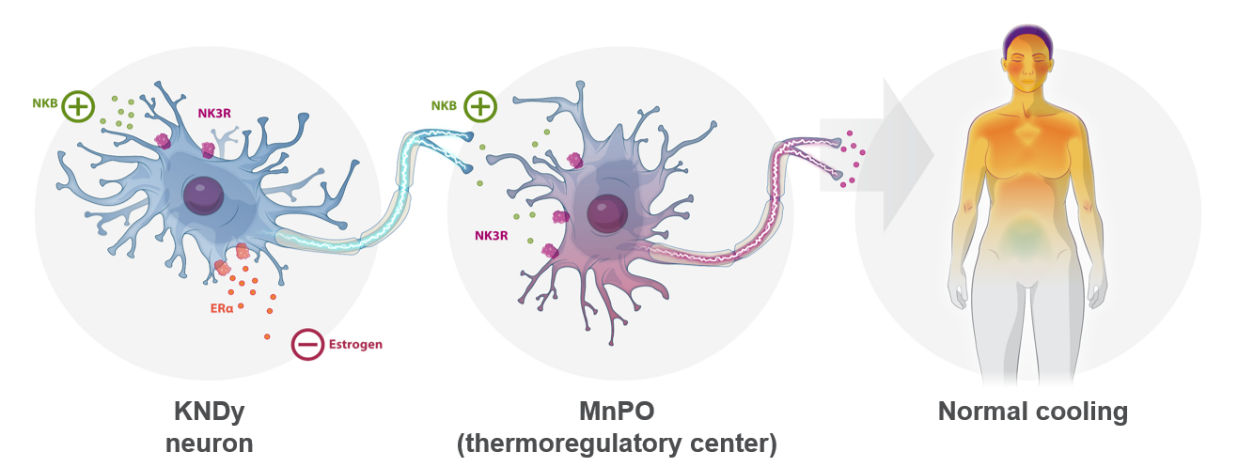
Figure 2. Disruption of thermoregulatory balance due to reduced estrogen
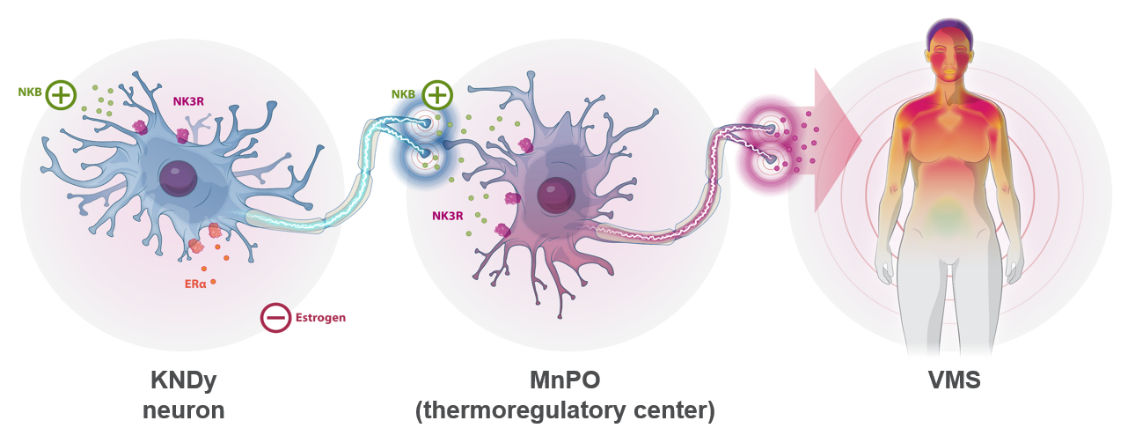
Figure 3. Mechanism of action of fezolinetant
Krajewski S, Burke M, Anderson M, et al. Forebrain projections of arcuate neurokinin B neurons demonstrated by anterograde tract-tracing and monosodium glutamate lesions in the rat. Neuroscience. 2010;166(2):680-697. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.053.
Padilla SL, Johnson CW, Barker FD, et al. A Neural Circuit Underlying the Generation of Hot Flushes. Cell Rep. 2018;24(2):271-277. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.037.
Dacks PA, Krajewski SJ, Rance NE. Activation of Neurokinin 3 Receptors in the Median Preoptic Nucleus Decreases Core Temperature in the Rat. Endocrinology. 2011;152(12):4894-4905. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1492.
Jayasena CN, Comninos AN, Stefanopoulou E, et al. Neurokinin B Administration Induces Hot Flushes in Women. Sci. Rep. 2015;5(1):8466. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08466.
Krajewski-Hall SJ, Blackmore EM, McMinn JR, Rance NE. Estradiol alters body temperature regulation in the female mouse . Temperature (Austin, Tex.). 2017;5(1):56-69. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1384090.
Ruka KA, Burger LL, Moenter SM. Both Estrogen and Androgen Modify the Response to Activation of Neurokinin-3 and κ-Opioid Receptors in Arcuate Kisspeptin Neurons From Male Mice. Endocrinology. 2016;157(2):752-763. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2015-1688.
Mittelman-Smith MA, Williams H, Krajewski-Hall SJ, et al. Role for kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in cutaneous vasodilatation and the estrogen modulation of body temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012;109(48):19846-19851. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211517109.
RANCE NE, McMULLEN NT, SMIALEK JE, et al. Postmenopausal Hypertrophy of Neurons Expressing the Estrogen Receptor Gene in the Human Hypothalamus*. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990;71(1):79-85. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-71-1-79.
Rance N, 3rd YW. Hypertrophy and increased gene expression of neurons containing neurokinin-B and substance-P messenger ribonucleic acids in the hypothalami of postmenopausal women. Endocrinology. 1991;128(5):2239-2247. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-128-5-2239.
Mittelman-Smith MA, Krajewski-Hall SJ, McMullen NT, Rance NE. Neurokinin 3 Receptor-Expressing Neurons in the Median Preoptic Nucleus Modulate Heat-Dissipation Effectors in the Female Rat. Endocrinology. 2015;156(7):2552-2562. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2014-1974.
Rance NE, Dacks PA, Mittelman-Smith MA, et al. Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons: A novel hypothesis on the mechanism of hot flushes. Front. Neuroendocr. 2013;34(3):211-227. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.07.003.
Krajewski-Hall SJ, Filipa MDS, McMullen NT, et al. Glutamatergic Neurokinin 3 receptor neurons in the median preoptic nucleus modulate heat-defense pathways in female mice. Endocrinology. 2019;(0013-7227) Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00934.
Dacks P, Rance N. Effects of estradiol on the thermoneutral zone and core temperature in ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 2010;151(3):1187-1193. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1112.
Tahara A, Tanaka-Amino K, Ohtake A, et al. Fezolinetant attenuates hot flash-like symptoms via inhibition of neuronal activity in the median preoptic nucleus in ovariectomized rats [abstract]. Menopause. 27:1467. Virtual. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/GME.0000000000001694.
Depypere H, Lademacher C, Siddiqui E, Fraser GL. Fezolinetant in the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2021;30(7):681-694. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2021.1893305.
The medical information on this website is for educational purposes only and is intended to provide scientific information about Astellas products. This information is not intended as medical advice or clinical recommendations. This website is for use only by United States residents and licensed healthcare professionals (HCPs) practicing in the United States. Product labeling may vary between countries.
Please choose an option that best describes you:
For visitors outside the United States: click here