Fezolinetant is contraindicated in individuals using CYP1A2 inhibitors, as they increase the plasma concentration and exposure of fezolinetant; however, the use of caffeine, a weak CYP1A2 inhibitor, was not restricted in Phase 3 clinical trials and baseline use did not impact efficacy or lead to an increase in adverse events
Figure 1. Difference in change from baseline to Week 12 in VMS frequency between fezolinetant groups and placebo by caffeine use at baseline.2
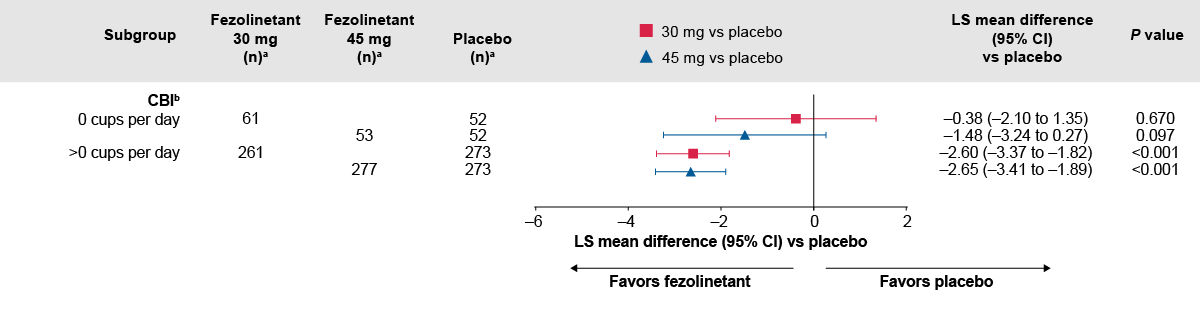
The number of participants with baseline data is shown.
P-values were calculated without multiplicity adjustment.
aAll randomized participants assessed according to the randomization at first dose. Total numbers of participants ‒ placebo: 342, fezolinetant 30 mg: 339; fezolinetant 45 mg: 341.
bA total of 17, 17, and 11 participants in the placebo, fezolinetant 30 mg, and fezolinetant 45 mg groups, respectively, had no caffeinated beverage intake data at baseline or any of the visits. If baseline caffeinated beverage intake was missing, but there was at least one caffeinated beverage intake result at any visit, then the missing baseline data were imputed in accordance with the study visit data.
CBI, caffeine baseline intake
Adapted from: Santoro NF, Menopause 2024.
Figure 2. Difference in change from baseline to Week 12 in VMS severity between fezolinetant groups and placebo by caffeine use at baseline.2
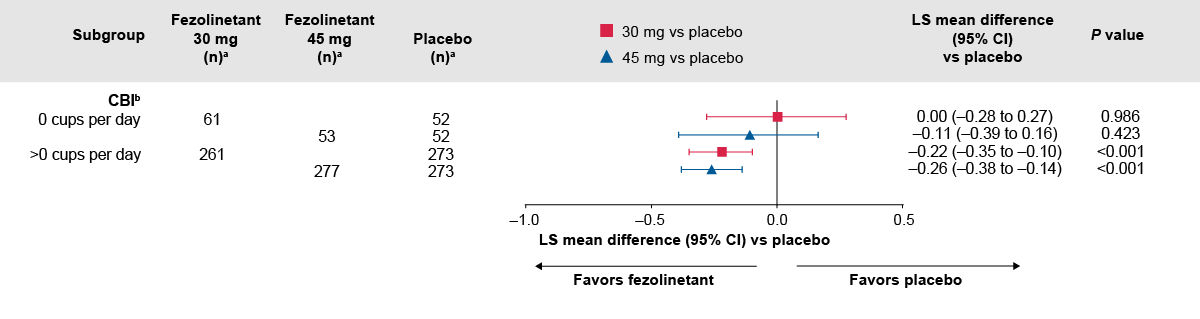
The number of participants with baseline data is shown.
P-values were calculated without multiplicity adjustment.
aAll randomized participants assessed according to the randomization at first dose. Total numbers of participants ‒ placebo: 342, fezolinetant 30 mg: 339; fezolinetant 45 mg: 341.
bA total of 17, 17, and 11 participants in the placebo, fezolinetant 30 mg, and fezolinetant 45 mg groups, respectively, had no caffeinated beverage intake data at baseline or any of the visits. If baseline caffeinated beverage intake was missing, but there was at least one caffeinated beverage intake result at any visit, then the missing baseline data were imputed in accordance with the study visit data.
CBI, caffeine baseline intake
Adapted from: Santoro NF, Menopause 2024.
Data on file.
Santoro N, Nappi R, Neal-Perry G, et al. Fezolinetant treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause: Effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in two phase 3 studies (SKYLIGHT 1 and 2). Menopause. 2024;31(4):247-257. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0000000000002340.
The medical information on this website is for educational purposes only and is intended to provide scientific information about Astellas products. This information is not intended as medical advice or clinical recommendations. This website is for use only by United States residents and licensed healthcare professionals (HCPs) practicing in the United States. Product labeling may vary between countries.
Please choose an option that best describes you:
For visitors outside the United States: click here